Atmosphere Optics, Spectroscopy and Lasers Laboratory LOA-SL
|
Polymer selforganization
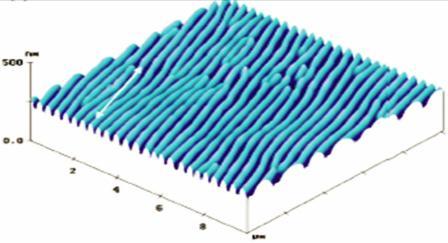
Research overview. The main research involve studies of some polymers with complex chemical structure, generate in solution and in solid state as thin films, aggregates of nanometer size. These nanometer structures offer the polymer outstanding properties with applications in non- conventional technologies. These applications are also favoured by the photochrome properties of some groups type trans-stiblene and diazo-benzene from the polymer chains of the compounds which are to be studied during the project development. The main part of the research is focussed on getting deep knowledge on the self-organization phenomenon and the processes that lead to the appearance of self-organized structures inside the photo-functional amorphous materials. For example, the photo-sensitivity of the polymers that contain diazo-benzene groups is of basic importance not only as a model of structure for studies concerning the energy absorption or as investigation source in self-organized systems, but also as photo-sensitive materials for the realization of devices with various applications in nanotechnologies [Georgeta Strat, M.Strat, S. Gurlui, C.Focsa, D. Dimitriu, Series: Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, titlul cartii: Self- Organization in Nanomaterials, Editors: Punit Boolchand, Gerald Lucovsky, M. Popescu, Editura INOE, 2007, p.53-91]. It is also known that certain derivates of cholesteryl form different types of molecular assemblies in aquaeus solutions, such as lyotrope structures of liquid crystals, micelles, ordered nano-layers, etc. The formation of these molecular assemblies is mainly the result of the molecular associations that appear due to the universal and specific molecular interactions [Georgeta Strat, Polymer Degradation and Stability, 76, 79-83, ( 2002 )]. The studies made evident still another aspect. In this type of polymers, the liotrope meso-phases can be also generated in solution if we choose, for instance a good solvent for the mesogene groups and a bed solvent for the polymer chain or the other way round. In this binary solvent mixtures, for example a polar solvent and a non-polar one, or a polar solvent and a less polar one, a critical concentration of one of the solvents appears such that the solvite, for example cholesteryl 6-(methacryloyloxy)hexanoate and a small amount of (1-pyrenylmethyl) 6-(methacryloyloxy)hexanoate (Py-C5-MA) generate molecular aggregates of the form [poly(Chol- C5-MA/Py-C5-MA)] [Shin- Ichi Yusa, Mikiharu Kamachi, Yotaro Morishima, SHIN-ICHI YUSA, J Polym Sci A: Polym Chem 37: 47 (1999)]. Knowledge of the processes that lead to the appearance of the self-organization phenomenon and, on this basis, of the nano-structures, is very important since it permits the controlled action at a molecular and atomic level during the operation of nanomaterial preparation. This control at atomic and molecular level is necessary for the development of new technologies able to work at a nano-scale in a controlled and reproducible manner, representing the basis for the future production processes. Many of these technologies, such as SPM (Scanning Probe Microscopy), were first developed in research laboratories, but we need to specify that they have not yet reached their entire potential [C. P. Poole and F. J. Owens, Introduction to the Nanotechnology (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003]. The ascending dynamics of practical applicability imposed the increase of the demand of conjugated polymers, soluble and processable as thin films. The creation of multi-functional materials directed toward various applications imposes an inter-disciplinary approach of the phenomena governing their properties, by getting together the knowledge from the fields of physics, chemistry and material science as modern working instruments. The theme approach is justified by the fact that the super-molecular ensembles posess well-defined characteristics, offering an alternative in the preparation of new materials, with specific properties in various applications [T. Takata, N. Kihara, Y. Furusho, Adv Polym Sci, 2004; 171; F. Huang, H.W. Gibson, Progr. in Polym.Sci., 2005, 30(10), 982]. The self-assemblage of molecules offers unique opportunities for applications in high performance fields, such as electronics, de-pollution and mass transfer or catalysis [A. Harada, Acta Polymerica, 1998, 49, 3]. The macroscopic properties of the assemblies are the result of the combination between the molecular structure and macroscopic organization in diverse conditions of temperature and environment. Polymer ablation still yields a big potential, even though it has a research field over 20 years. Although, generally commercially known available polymers such as polyamide (KAPTON, APICAL, UPILEX), polymetilmetacrylate (MAKROFOL), polyester (MYLAR), etc that are applied in extensive papers, both for fundamental and applicative research area, make them unsuitable for high quality structuring, e.g. low sensitivity, carbonization upon radiation, redeposition of ablated melting material on the polymer structure surface, etc. [T. Lippert, M. Hauer, C.R. Phipps and A. Wokaun, Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 77 (2003), pp. 259–264] The laser polymer ablation mechanism is a complex interrelated system where the photochemical and phototermal reactions are very important. Photochemical decomposition is intrinsically capable of higher spatial resolution because thermal damage to the surrounding material is minimal and explains many futures of laser ablation, especially in the low fluence range. A study concerning the surface structuring capacity of the polymers showed that the irradiation conditions significantly influence the surface geometry of the polymers.For example, the photo-sensitivity of the polymers that contain diazo-benzene groups is of basic importance not only as a model of structure for studies concerning the energy absorption or as investigation source in self-organized systems, but also as photo-sensitive materials for the realization of devices with various applications in nanotechnologies.Surface irradiation was carried out under the action of an optical radiation field with a controlled distribution represented by an interference pattern of electromagnetic radiation beams. The explanation of the surface patterning in azo-polymer materials as on optical -mechanical effect is quite true it take into account the well known concept of the self- structuring and self-organizing phenomena [G. Strat, M. Strat, S. Gurlui, C. Focsa, D. Dimitriu, Self organization in nanomaterials, Ed. INOE, 5, 53 (2007); Stephen J. Blundell, Katherine M. Blundell Concepts in Thermal Physics. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0198567707.(2008)].Self- organization and spontaneous ordering into the periodic structure can be found in different fields of science. As an example, plasma is a strong nonlinear medium, very suitable for the development of self-organized structures inside it. PUBLICATIONS
|