Atmosphere Optics, Spectroscopy and Lasers Laboratory LOA-SL
|
ENIAN - Enhanced ion acceleration by laser irradiation of special thin polymers layers containing nanoparticles Contracting authority: INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC PHYSICS – IFA , Funding: Ministry of Education and Research , Contract no: FAIR_09 / 24.11.2020 / 2020-2023/ Budget 1.600.000 lei ( ~328.220) euro Project Manager: Assoc. Prof. PhD. Habil. Silviu-Octavian GURLUI
The goal of the ENIAN project is based on two main directions: a) to study the fundamental aspects that characterize the interaction between the laser beam and polymers targets/ nanoparticle doped polymers via experimental methods and to develop a new theoretical model that describes processes (solid state changes after irradiation, plasma generation and expansion behavior, etc.); b) to improve the properties of the designed targets by means of PLD optical diagnosis, to reduce the contamination of the plasma, to enhanced ion acceleration.
ENIAN project includes one of the highest technology necessary for the doping of thin composite layers (100-1000 nm) with nanoparticles (10-100 nm) in special experimental conditions (using 100 micron thick plastic substrate) that offer a wide range of critical parameters (vacuum, geometry, temperature, optical properties, roughness, thickness, etc.). Using the prototype of the new targets designed in Romania for standard laser target holders (FAIR) and characterize them, PLD composite layers will be both the core of further advanced research on hydrodynamic expansion simulation and to improve the quality of targets for x-ray generation in laser-plasma interactions. Optical and electrical properties of the laser produced plasma and ion acceleration in the both BPA and TNSA regimes depend strongly by the laser parameters (the pulse energy, the laser fluence, the pulse width, the laser repetition rate), the irradiation conditions (size of the focal point, the presence of the pre-pulse) and the target composition and geometry (the target thickness, multilayer’s, nanostructures, etc). In order to increase the laser energy absorption in the thin foils and the transfer of the laser light energy to the plasma, advanced targets will be further developed according needed FAIR infrastructure projects (APPA/MML/Plasma Physics/PHELIX ). Furthermore, optimal target thickness and embedded NPs types in the polymer target must be analyzed according to the light absorption coefficient in the wavelength range from UV to near IR. Used embedded metallic NPs and PLD thin layer deposed on the polymers films permit to increase the laser absorbance in thin targets.
To enhance the efficiency of the laser-solid interactions, laser- plasma plume interactions and the atomic emission intensity, Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) dual-pulse will be investigated: ICCD monitoring of the global dynamics of the plasma plume, velocities determination of the structures that form the generated plasma; Time and space resolved optical emission spectroscopy: element identification, determination of the velocities of the generated species, plasma contamination effect under the wall irradiation, resolved space-time excitation temperature and electron density profiles; Electrical characterization of the plasma plume: plasma potential measurements with emissive probes heated by a focused infrared laser beam; Develop a theoretical model to describe the implicated processes in plasma generation and expansion in PLD.
ENIAN project is based on the use of research infrastructures and human resources in Romania and Germany, both experimental resource (FAIR & LOASL) and simulations - hydrodynamic expansion simulation (PIC codes to simulate the interaction/ at FAIR supercomputers) to achieve special goals for the development of FAIR research infrastructure, to improve the needed laser beam transport in vacuum and for expanding of research and applications in the field of plasma and high energy particles. ENIAN is based on two main directions: a) to study the fundamental aspects that characterize the interaction between the high fluency laser ablation and solid state material via experimental methods and to develop a new theoretical model that describes the fundamentals (solid state changes after irradiation, plasma generation and expansion behavior, etc.); b) to improve the properties of the composited targets by means of PLD and space-time resolved transitory laser ablation plasma. General project objectives: To increase the knowledge in an inter-disciplinary, up to date field, promote and characterize new materials; Raise the standards of the inter-disciplinary basic research, through the co-operation of a critical mass of researchers from FAIR and LOA-SL/UAIC and other high education institutes; Efficiently exploit the existing resources of our laboratories; Improve the performances of the research staff at a national/international level, to integrate young researchers/PhD in the project team; Provide a specialization of researchers through training stages, prestigious high education institutes; Increase the visibility at a national and international level, by disseminating the project results to the scientific and economical community, as well as to an extended public; Provide a co-operation and a long-term utilization of the obtained results much beyond the project period.
Specific project objectives n Preparation of advanced targets to realize absorption measurements test of ion acceleration, at low energy, of ion yield emission and production of absorbent metallic nanostructures and nanoparticles; n Optical properties characterization of both the bulk targets and nanoparticles coated and embedded on polymers targets; n Study of the double laser pulse interacting under laser fluencies above 1010 W/cm2 with bulk and embedded metallic nanoparticle polymers (EMNP) targets in BPA regime to produce high ion emissions (below 1 MeV) and high current; n Study of the advanced EMNP targets behavior under laser fluencies above 1015 W/cm2 to accelerate TNSA ions with kinetic energies above 1MeV/charge state; n Study the radiation pressure acceleration (RPA) under laser fluence above 1015 W/cm2 to obtaining very high ion acceleration above 10 MeV/charge state. n Modeling of the laser - EMNP targets interactions by means COMSOL multyphysics software n Performing PIC codes (using FAIR infrastructure) to investigate the interaction & simulation hydrodynamic expansion n M aking prototype targets on standard laser target holders used at FAIR and characterize them by means: space-time resolved optical emission spectroscopy, UV-VIS/FTIR spectroscopy, XRD, XPS, AFM, scanning electron microscopy SEM/ EDX/EDS n Contributing to improve the vacuum technology for laser beam transport
Report 2023 (link here)
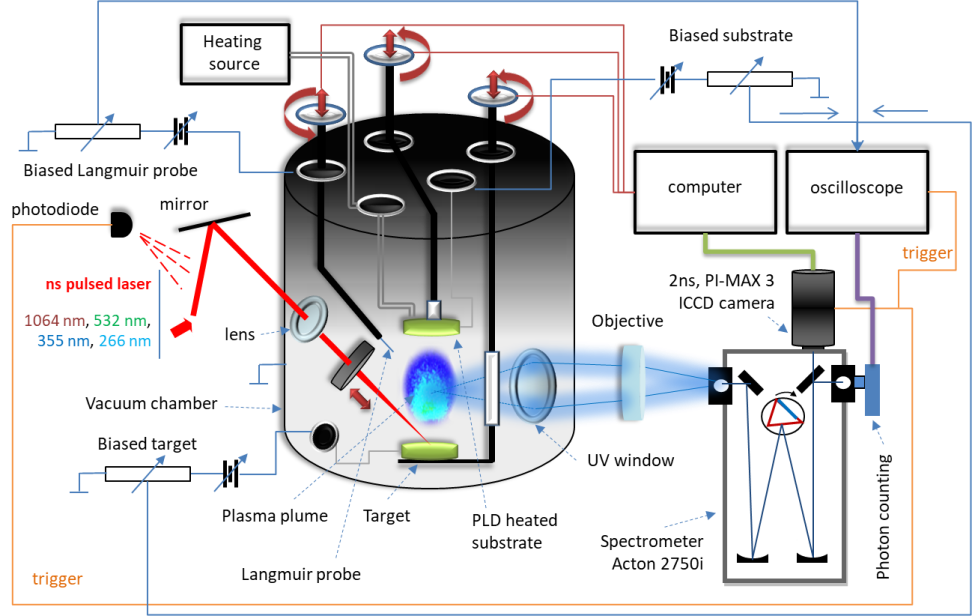
The research to study the e nhanced ion acceleration by laser irradiation of special thin polymers layers containing nanoparticles was carried out by the LOASL team (http://spectroscopy.phys.uaic.ro/) both through numerical simulations in COMSOL as well as through experimental studies carried out in the vacuum chamber of the laser installation of the laboratory with laser systems YG 981E/IR-10 and at working parameters (30-150 mJ energy, 532 nm wavelength of laser radiation, 10 ns duration pulse, 10 Hz repetition frequency). The precursor materials (targets) as well as those obtained as thin layers by the PLD (Pulsed Laser Deposition) technique were analyzed by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy - FTIR spectroscopic methods; Laser Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy - LIF; Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy -EDX, UV-Vis Spectroscopy) and optical, electronic (Scanning Electron Microscopy - SEM) and atomic force microscopy (Atomic Force Microscopy - AFM) methods. In a first stage, numerical model was developed for the simulation in COMSOL. The theoretical analysis carried out in this way on various materials showed through the obtained results the complexity of the phenomena contributing to the development of high temperatures in the target material. A numerical model for simulation with Finite Element Method in COMSOL was developed in the first stage. Experimental studies assisted by numerical modeling in COMSOL followed, as well as by simulation in GAUSSIAN 6 performed on metallic Ag materials [1,2] and on natural polymeric bicomposite materials [3-6]. The results of the study of laser ablation applied to the hemp stalk, which resulted in the transfer of identical material in the deposited thin layer [5] led to the conclusion that in the hemp stalk both the components and the structure of their deposition in the biocomposite led to a "homogenization" of the laser effect on the biocomposite, regardless of the optical, kinetic, thermal, properties of each individual component. In other words, the hemp stalk behaved as a composite material also in the process of laser ablation and deposition within the PLD technique. As a result, the increased ablation yield was found both experimentally and by COMSOL simulation of composite components compared to individual components [6]. Such effects have also been observed for other biocomposite materials, but with side chain modifications of the constituent polymers (demethoxylation of curcumin, deacetylation of chitin) [4,5]. A contribution to a better understanding of the phenomena and interaction in natural composite structures was also brought by the study of some rock fragments of meteoritic origin [7]. These studies carried out on natural composites and especially the one performed on the hemp stalk led to the idea of manufacturing biomimetic targets by following the changes in the effects of laser radiation depending on the composition of the composite matrix and the dispersed metallic phase. Studies performed on the targets fabricated on biomimetic models have shown major changes in ablation and particle kinetics in the ablation plasma resulting in thin layers with changes not only in composition but also in phase (liquid versus solid). These results were reported and presented in the scientific communications organized by the project team and will be disseminated separately in publications mentioning the funding project as was done in the case of already published results [1-7]. The experimental and numerical simulation study of the interaction of radiation with natural polymeric biocomposite materials and the results of ablation and deposition in thin layers is an absolute novelty, being the first time it was carried out in the LOASL laboratory [8], constituting the starting element in the idea for the research within the project of the face. The idea of manufacturing biomimetic targets after the model of natural biocomposites is also completely new and was developed in the LOASL laboratory during the ENIAN project research. The variety of biocomposite materials required a prior analysis both by numerical simulation and by various analyzes to identify biocomposites of interest in terms of composition and complexity of morphological structures to achieve the expected results. The publication of the results in scientific articles attracted the interest of researchers (by accessing the respective articles and citing them) as well as that of the editors of scientific publications and that of the organizers of international conferences, thus benefiting, as co-authors, from numerous invitations for publication and scientific communications.
REFERENCES [1] Alexandru Cocean, Iuliana Cocean, Georgiana Cocean, Cristina Postolachi, Daniela Angelica Pricop, Bogdanel Silvestru Munteanu, Nicanor Cimpoesu and Silviu Gurlui, Study of Physico-Chemical Interactions during the Production of Silver Citrate Nanocomposites with Hemp Fiber, Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102560 [2] A. Cocean, I. Cocean and S. Gurlui, INFLUENCE OF THE IMPURITIES TO THE COMPOSITE MATERIALS IN LASER ABLATION PHENOMENA, U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 83, Iss. 3, 2021 [3] A. Cocean, I. Cocean, N. Cimpoesu, G. Cocean, R. Cimpoesu, C. Postolachi, V. Popescu and S. Gurlui, Laser Induced Method to Produce Curcuminoid-Silanol Thin Films for Transdermal Patches Using Irradiation of Turmeric Target, Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(9), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11094030 [4] Georgiana Cocean, Alexandru Cocean, Cristina Postolachi, Silvia Garofalide, Georgiana Bulai, Bogdanel Silvestru Munteanu, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Iuliana Cocean and Silviu Gurlui, High-Power Laser Deposition of Chitosan Polymers: Medical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1537. https:// doi.org/10.3390/polym14081537 [5] Cocean, A.; Cocean, G.; Diaconu, M.; Garofalide, S.; Husanu, F.; Munteanu, B.S.; Cimpoesu, N.; Motrescu, I.; Puiu, I.; Postolachi, C.; Cocean, I. and Gurlui, S. Nano-Biocomposite Materials Obtained from Laser Ablation of Hemp Stalks for Medical Applications and Potential Component in New Solar Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043892 [6] Cocean, G.; Cocean, A.; Garofalide, S.; Pelin, V.; Munteanu, B.S.; Pricop, D.A.; Motrescu, I.; Dimitriu, D.G.; Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S. Dual-Pulsed Laser Ablation of Oyster Shell Producing Novel Thin Layers Deposed to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Polymers 2023, 15, 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193953 [7] Alexandru Cocean, Cristina Postolachi, Georgiana Cocean, Georgiana Bulai, Bogdanel Silvestru Munteanu, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Iuliana Cocean and Silviu Gurlui, The Origin and Physico-Chemical Properties of Some Unusual Earth Rock Fragments, Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 983. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12030983 [8] I. Cocean, A. Cocean, C. Postolachi, V. Pohoata, N. Cimpoesu, G. Bulai, F. Iacomi, S. Gurlui, Alpha keratin amino acids behvior under high fluence laser interaction. Medical applications, Applied Surface Science 488 (2019) 418–426, DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.207
List of Publications
1. Cocean, A.; Cocean, G.; Diaconu, M.; Garofalide, S.; Husanu, F.; Munteanu, B.S.; Cimpoesu, N.; Motrescu, I.; Puiu, I.; Postolachi, C.; Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S. Nano-biocomposite materials obtained from laser ablation of hemp stalks for medical applications and potential component in new solar cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043892 2. Kadri, L.; Abderrahmane, A.; Bulai, G.; Carlescu, A.; Doroftei, C.; Motrescu, I.; Gurlui, S.; Leontie, L.; Adnane, M. Optical and structural analysis of TiO2-SiO2 nanocomposite thin films fabricated via pulsed laser deposition technique. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13101632 3. Sprincean, V.; Leontie, L.; Caraman, I.; Lupan, O.; Adeling, R.; Gurlui, S.; Carlescu, A.; Doroftei, C.; Caraman, M. Preparation, chemical composition, and optical properties of (β-Ga2O3 composite thin films)/(GaSxSe1-x lamellar solid solutions) nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142052 4. Cocean, G.; Cocean, A.; Garofalide, S.; Pelin, V.; Munteanu, B.S.; Pricop, D.A.; Motrescu, I.; Dimitriu, D.G.; Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S. Dual-pulsed laser ablation of oyster shell producing novel thin layers deposed to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Polymers 2023, 15, 3953. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15193953 5. Balbarau, A.; Ivanescu, L.M.; Martinescu, G.; Rimbu, C.M.; Acatrinei, D.; Lazar, M.; Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S.; Cocean, A.; Miron, L. Septicemic outbreak in a rainbow trout intensive aquaculture system: Clinical finds, etiological agents, and predisposing factors. Life 2023, 13, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13102083
Conferences
1. Alexandru Cocean, Georgiana Cocean, Silvia Garofalide, Vasile Pelin, Dana Angelica Pricop, Bogdanel Silvestru Munteanu, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Dan Gheorghe Dimitriu, Iuliana Cocean and Silviu Gurlui, Numerical simulation in assisting the experimental study as a tool for estimating the working parameters, anticipating and explaining the experimental results. COMSOL Multiphysics and Gaussian 6 software, Conferința FTEM (Fizica și Tehnologiile Educaționale Moderne) 20 mai 2023, http://ftem.faculty.ro/ 2. Georgiana Cocean, Alexandru Cocean, Silvia Garofalide, Cristina Postolachi, Maria Diaconu, Francisca Husanu, Bogdanel Silvestru Munteanu, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Iuliana Motrescu, Ioan Puiu, Iuliana Cocean and Silviu Gurlui, Hemp stalk components transfer into composite nanostructures under high power pulsed laser ablation and deposition to produce functional materials, Conferința FTEM (Fizica și Tehnologiile Educaționale Moderne) 20 mai 2023, http://ftem.faculty.ro/ 3. Daniela Pricop, Silvia Garofalide, Alexandru Cocean, Iuliana Cocean, Vasile Pelin, Silviu Gurlui, Historical buildings degradation as an effect of chemical contaminants from anthropogenic pollution sources, Conferința FTEM (Fizica și Tehnologiile Educaționale Moderne) 20 mai 2023, http://ftem.faculty.ro/ 4. Cocean, A.; Postolachi, C.; Cocean, G.; Garofalide, S.; Diaconu, M.; Pelin, V.; Pricop, D.A.; Munteanu, B.S.; Motrescu, I.; Dimitriu, D.; Cocean, I. and Gurlui, S.; Detection of IR vibration bands in environmental analysis using GAUSSIAN 6 software, 4th International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/), 25-28 iulie 2023, online poster session (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/program/). 5. Cocean, G.; Cocean, A.; Postolachi, C.; Garofalide, S.; Pricop, D.A.; Munteanu, B.S.;Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S.; Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy technique used to identify photo-chemical processes during laser ablation of hemp stalk, 4th International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/), 25-28 iulie 2023, online poster session (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/program/). 6. Postolachi, C.; Cocean, A.; Cocean, G.; Garofalide, S.; Pricop, D.A.; Munteanu, B.S.; Cimpoesu, N.; Motrescu, I.; Cocean, I.; Gurlui, S.; High pulsed laser energy to produce structural morphology of thin layers for green chemical processes, 4th International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/), 25-28 iulie 2023, online poster session (https://photocatalysis-workshop.eu/program/). 7. Cocean, A.; Motrescu, I.; Bulai, G.;, GArofalide, S.;, Pricop,D.; Pelin, V.; Cocean, G.; Diaconu, M.; Postolachi, C.; Husanu, F.; Pata, D.; Ababei, R.; Munteanu, B.; Cimpoesu, N.; Puiu, I.; Dimitriu, D.; Cocean, I.;Gurlui, S. Natural and anthropogenic phenomena that have played an important role in Romania in the last 5 years, European Lidar Conference ELC 2023,Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 13.09.2023-15.09.2023, https://enviro.ubbcluj.ro/european-lidar-conference-2023/ - prezentare Silviu Gurlui 8. ZILELE ACADEMICE IEŞENE, Ediţia a XXXVIII-a, Sesiunea științifică națională Vectori ai dezvoltării rurale în Regiunea Nord-Est a României (ediția a III-a) Sisteme agroalimentare durabile 12 octombrie 2023, Alexandru Cocean, Georgiana Cocean, Cristina Postolachi, Silvia Garofalide, Diana Manuela Lina, Vasile Pelin, Maria Diaconu, Daniela Angelica Pricop, Răzvan Ababei, Dan Gheorghe Dimitriu, Bogdănel Silvestru Munteanu, Georgiana Bulai, Nicanor Cimpoeșu, Iuliana Motrescu, Ioan Puiu, Iuliana Cocean and Silviu Gurlui, Tehnologia de vârf bazată pe interacțiunea laserului cu materia implicată în dezvoltarea economiei rurale. Aplicabilitatea acesteia pe termen scurt și pe termen lung /Cutting-edge technology based on the interaction of laser with matter involved in the development of rural economy. Its short-term and long-term applicability; Sesiunea științifică a avut loc online, în data de 12 octombrie 2023, între orele 9:30 – 16:30, pe platforma Zoom. https://us02web.zoom.us/j/83863323372?pwd=UDNmV1NJM3F5eEJ4SHR0Y1h1cFExZz09; Meeting ID: 838 6332 3372; Passcode: 941046-prezentare Iuliana Cocean
Report 2021 (download in pdf format, here) 1. Study of the interaction of the laser beam with target by means of Finite Element Method The numerical study interaction of the laser beam with the target offers information on the impact of the laser parameters and target material characteristics on developing processes based on the phenomena indicated by the simulation results. For this purpose, finite element analysis is the method that fits best. There are two software variants that we have in mind, namely COMSOL and PIC. In a first stage, we used the COMSOL software to study the phenomena, processes and conditions obtained for the generation of ablation plasma, the Particle in cell (PIC) software being more suitable for the study of plasma movement and the particles that compose it, i.e. for the subsequent stage of study. Laser interaction with the silver target containing Fe and Ni impurities was numerically simulated and the results were used to explain the Experimental phenomena noticed on the thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition technique. It resulted that the three instabilities, Plateau – Rayleigh instability (PRI), Rayleigh – Taylor instability (RTI), Richtmyer – Meshkov instability (RMI), and the “crown splash”, as phenomena related to fluids break-up are are responsible for the formation of droplets during the deposition of thin metal films. The explanation is based on the results obtained in COMSOL which indicates the formation of both the liquid phase and the gas and plasma during laser irradiation of the target. The fluid phase is highlighted by the point temperatures developed on the spot and in its immediate vicinity, over a distance until which the thermal diffusion takes place depending on the material characteristics.If the thermal energy developed on the spot that interacts with the laser radiation is also dependent on the laser parameters, as well as on the optical characteristics of the target material, the heat transfer on the surface of the material in the vicinity of the spot depends only on the thermal conductivity characteristics. Heat transfer in the target volume will be influenced by laser beam over a distance equal to the optical path (inverse of the absorption coefficient) and under the exponential attenuation effect given by the Beer-Lambert law, after which only the characteristics related to the thermal conductivity of the material will count.The same parameters for the numerical simulation and for the experimental proceedings were used: pulse energy of 100 mJ, 150 mJ and 180 mJ, 10 ns pulse width, 10 Hz pulse repetition and 168 μm spot radius and 10-2 Torr pressure in the deposition chamber. Parametric sweep was used to vary the pulse energy. The theory, mathematics and formulae to describe the physical phenomena and processes and their implementation in COMSOL simulation is as described in the articles previously published by our laboratory team [2, 3]. New conditions and extended geometry and domains have been added with this simulation to analyse and anticipate thermal behaviour and heat transfer when plasma of ablation travels from the target to the substrate and the new model was published by our laboratory [1]. The geometry includes the target and the environment surrounding the target in the deposition chamber, as well as the non-homogeneous material of the target (Figure 1) [1].
Figure 1. Geometry with materials and mesh for COMSOL simulation [1]. The results are collected in the nodes as per the mesh which is set-up as “extremely fine” for the areas of interest and “coarse” for the rest of geometry in order to optimize the data accuracy versus computing time. The acquired data are used to obtain phase change diagrams T (d) on the target in spot and its vicinity, as much as heating takes place.
Figure 2. Phase change diagrams T (d) on the target irradiated surface after 10 ns for: iron and nickel at different energies (a) and their co-existing phases at 150 mJ (b); silver at different energies (c) and its co-existing phases at 150 mJ (d) [1]
The silver melting and boiling points, as well as those of the impurities of iron and nickel are used as reference for phase change in the diagrams. Phase components are analyzed in the diagrams of Figure 3 [1]. The thermal effects in the deposition chamber were analyzed by isosurface diagrams and 2 D plots as presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
Figure 3. Study of phases fractions during ablation, for t = τ = 10 ns, based on COMSOL simulation. (a) Phase rate per element developed during laser ablation at 150 mJ on COMSOL simulation; (b) Phase rate out of total ablated material based on COMSOL simulation; (c) Element rate out of each phase during ablation to different energies based on COMSOL simulation [1]
Figure 4. 3D Plot representing the Isosurface where heating is high enough to favor the plasma formation on the target and heat transfer in the surrounding environment [1]
Figure 5. 2D Heating plots in xOy plane at 10 ns when using 150 mJ laser energy: a) on the target surface; b) at 10 mm height from target; c) at 20 mm height from target [1]
Conditions for existence of different phases of ablated material in the deposition chamber on the plasma plume trajectory are analyzed in phase diagrams as in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Thermal effects in the deposition chamber target surrounding atmosphere in (x, y, z) = (0, 0, z) and z Є [0, d] and d=20 mm (distance between target and support) [1]
The fluid phases developed due to thermal effects during laser interaction with the target material explain droplets formation in terms of instabilities of PRI, RTI and RMI type, as well as crown splash fluid break-up at the impact with the solid substrate or still melted film on the substrate. Thin film deposition for experimental study to compare with simulation results was conducted on the installation presented in Figure 7. The laser system used was YG981E/IR- 10 Hz, and the parameters: τ=10 ns pulse width, λ=532 nm wavelength, α=45° incident angle and ν = 10 Hz pulse repetition time (Figure 1). The pressure in the deposition chamber was 3·10-2 Torr. The SEM images of figure 7 evidence different shapes of droplets, each being specific to a certain pulse energy of the laser beam in interaction with the silver target doped with Fe and Ni impurities, and that corresponds to certain amounts (percentage) of liquid, gas or plasma in the total fluid phase, each being susceptible to one or another of the fluid break-up instabilities.
Figure 7. Compared SEM images of droplets on the thin films A (180 mJ) and B (100 mJ): (a) Sample A (180 mJ) 500x; (b) Sample A (180 mJ) 5kx; (c) Sample B (100 mJ) 500x; (d) Sample B (100 mJ) 5kx [1]
“These instabilities are based on the induced perturbing phenomena such as electromagnetic field of laser beam for the first 10 ns, the electric field of the diffusion current generated by the charged carriers (ions in plasma) during their motion and the phase states developed during ablation and evidenced in the numerical simulation in COMSOL” [1]. Crown splash effect is noticed for high energy of 180 mJ (Figure 7 a) and b) while pearl shaped droplets are noticed for lower pulse energy (100 mJ). Study of the influence of each fluid-break-up phenomena and instabilities will provide with information and answers for finding solutions to diminish and avoid droplets formation or or on the contrary, to control their size and shape when they are aimed to be obtained.
Numerical study of CdO/Se and CdS/Se dual targets to synthesis CdSe nanoparticles on glass slab or other supports by PLD technique
Modeling and simulation of physical and chemical phenomena has an important role in obtaining information leading to a reduction in the number of experimental trials. In this sense, for the preparation of the conditions for deposition with pulsed laser of some quantum dots of cadmium selenide (CdSe), the study of the fulfillment of the ablation conditions of the precursor materials was performed with finite element method, using COMSOL analytical software platform. The method of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) of thin layers and obtaining nanoparticles represents the prospect of developing clean, ecofriendly technologies. Irradiation of the dual targets in the ablation and PLD process is studied for 532 nm laser beam wavelength, 150 mJ energy on a spot of 0.650 mm, pulse width of 10 ns and 10 Hz frequency. Ablation is studied according to the phase diagrams obtained as a result of modeling and simulation in COMSOL, in terms of temperatures relative to boiling points which represent the vaporization temperature (boiling point) in the case of Se and sublimation and decomposition in the case of CdO and CdS.
Figure 1. Isosurface thermal effects at pulse width ( 2 0 ns) in the target with zoom on spot
The ablation compared efficiency is also observed from the phase diagrams in which the temperature is represented in time and when it is observed that from the 20 ns how much the heating of the irradiated spot takes place under the action of the 10 ns pulse. It follows from the simulation that reaching the boiling points is more efficient for the dual target CdO / Se compared to the dual target CdS / Se. The results are presented in phase diagrams and plots in the Figures 1. Irradiation of the dual targets in the ablation and PLD process is studied for 532 nm laser beam wavelength, 150 mJ energy on a spot of 0.650 mm, pulse width of 10 ns and 10 Hz frequency (Figures 2).
Figure 2. Phase diagrams under different cut lines in pulse width
The ablation compared efficiency is also observed from the phase diagrams in which the temperature is represented in time and when it is observed that from the 20 ns how much the heating of the irradiated spot takes place under the action of the 10 ns pulse. It follows from the simulation that reaching the boiling points is more efficient for the dual target CdO / Se compared to the dual target CdS / Se. The simulation in COMSOL, however, predicts that only CdO has the necessary properties to interact with laser radiation efficiently and in the presence of selenium.
ISI Papers: [1]. Cocean, A., Cocean, I., Cocean, G., Postolachi, C., Pricop, D.A., Munteanu, B.S., Cimpoesu, N., Gurlui, S., Study of physico-chemical interactions during the production of silver citrate nanocomposites with hemp fiber, (2021), Nanomaterials, 11 (10), art. no. 2560 [2]. Cocean, A., Cocean, I., Cimpoesu, N., Cocean, G., Cimpoesu, R., Postolachi, C., Popescu, V., Gurlui, S., Laser induced method to produce curcuminoid-silanol thin films for transdermal patches using irradiation of turmeric target, (2021) Applied Sciences (Switzerland), 11 (9), art. no. 4030 [3]. Cocean, A., Cocean, I., Gurlu, S., Influence of the impurities to the composite materials in laser ablation phenomena, (2021), UPB Scientific Bulletin, Series A: Applied Mathematics and Physics, 83 (3), pp. 225-238 [4]. Kadri, L., Bulai, G., Carlescu, A., George, S., Gurlui, S., Leontie, L., Doroftei, C., Adnane, M., Effect of target sintering temperature on the morphological and optical properties of pulsed laser deposited TiO2 thin films, (2021), Coatings, 11 (5), art. no. 561 [5]. Catalin Panaghie, Ramona Cimpoesu, Bogdan Istrate, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Mihai-Adrian Bernevig, Georgeta Zegan, Ana-Maria Roman, Romeu Chelariu and Alina Sodor, New Zn3Mg-xY Alloys: Characteristics, Microstructural Evolution and Corrosion Behavior, Materials 2021, 14, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102505
Conferences [1]. Alexandru COCEAN , Iuliana COCEAN, Georgiana BULAI, Cristina POSTOLACHI, Bogdan MUNTEANU, Nicanor CIMPOESU, Silviu GURLUI, Invited Conference, Trace elements Photo-Analysis for environmental applications: a case study, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [2]. Alexandru COCEAN, Dorin BOTOC, Monica SIROUX, Cristina POSTOLACHI, Iuliana COCEAN, Silviu GURLUI, AMC-COMSOL: the new finite element technique to increase solar cell conversion, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [3]. Cristina POSTOLACHI, Mirela SUCHEA, Ioan-Valentin TUDOSE, Alexandru COCEAN, Iuliana COCEAN, Bogdanel Silvestru MUNTEANU, Nicanor CIMPOESU and Silviu GURLUI, Quantum Dots Pulsed Laser Deposition – a new simulation technique, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [4]. Iuliana COCEAN, Alexandru COCEAN, Cristina POSTOLACHI, Bogdanel Silvestru MUNTEANU, Nicanor CIMPOESU and Silviu GURLUI, High pulsed-laser effect on the hemp composite – advanced materials, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [5]. Silviu GURLUI, Alexandru COCEAN, Cristina POSTOLACHI, Georgiana COCEAN Iuliana COCEAN, Light interaction, pollution and SARS-Cov2: protection Mask biocompatibility-overview, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [6]. Alexandru COCEAN, Iuliana COCEAN, Cristina POSTOLACHI, Georgiana COCEAN and Silviu GURLUI, Laser induced chitin deacetylation- cutting-edge technology for “natural biological waste, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [7]. Cristina POSTOLACHI, Mirela SUCHEA, Ioan-Valentin TUDOSE, Alexandru COCEAN, Iuliana COCEAN, Bogdanel Silvestru MUNTEANU, Nicanor CIMPOESU and Silviu GURLUI, CdSe Quantum Dots insertion effect on the alpha-keratin PLD-thin films, The 3rd International Workshop Advances on Photocatalysis including Environmental and Energy Applications AdvPhotoCat-EE 2021, June 28-29, 2021 [8]. A. Cocean, I. Cocean, G. Cocean, C. Postolachi, B. Munteanu, N. Cimpoesu, S. Gurlui, Keratin-based polymer nanofilm membranes for medical applications, 13th International Conference on Physics of Advanced Materials (ICPAM-13), September 24 – 30, 2021, at the Hotel Eden Roc by Brava Hoteles, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Costa Brava, Spain [9]. C. Postolachi, A. Cocean, I. Cocean, G. Cocean, B. Munteanu, N. Cimpoesu, S. Gurlui,Study of Si/SiO2 core/shell Quantum Dots produced by Pulsed Laser Deposition, 13th International Conference on Physics of Advanced Materials (ICPAM-13), September 24 – 30, 2021, at the Hotel Eden Roc by Brava Hoteles, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Costa Brava, Spain
|